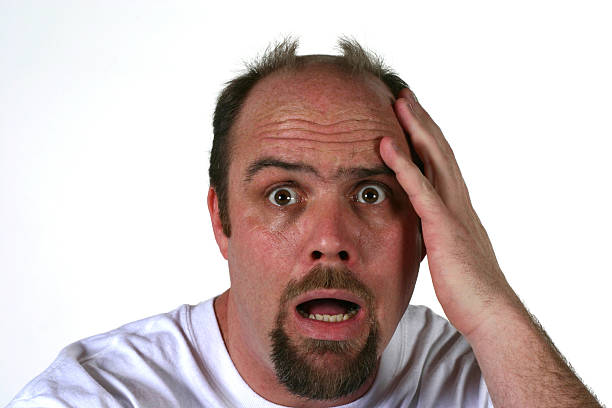
Diffuse thinning is a type of hair loss that affects your entire scalp hair. Unlike male pattern baldness, it doesn’t follow a specific pattern or cause a receding hairline or thinning on the crown.
Diffuse thinning can be caused by stress, medical conditions, or genetics. It can also be a side effect of certain medications, or simply a result of aging.
It’s important to note that diffuse thinning is not the same as balding. While it can cause hair loss, it doesn’t always lead to bald spots on your scalp.
If you want to know more about diffuse thinning and how to stop it from getting worse, read on for everything you need to know about this distressing type of hair loss…
Table of Contents
Key Takeaway:
Diffuse thinning is the slow, progressive, and often invisible loss of hair that can occur on any part of the head, including but not limited to the frontal and temporal regions. It is a very common condition that affects men and women alike.
Finding support from friends and family members can help with the stress associated with hair loss and make it easier to manage.
You can do several things to prevent diffuse thinning and stop the progression of hair loss. Eating a nutritious diet that includes plenty of vitamins and minerals, getting enough sleep, and protecting your hair from sun damage are all ways to prevent diffuse thinning from happening. You may consider talking to a professional by booking an appointment if you experience a severe form of thinning.
What is Diffuse Thinning Hair Loss?
As the name suggests, diffuse thinning hair loss occurs throughout the scalp. This type of hair loss generally progresses slowly, causing thinning over time. It is not the same as male pattern baldness, which causes a receding hairline and thinning of the crown.
It can be caused by genetics, medical conditions, stress, childbirth, certain medications, and hormone imbalances, among other things. It typically affects thin hair more than thick hair because thinner hair is more prone to breakage.

Causes of Diffuse Thinning
The common causes of diffuse thinning hair loss in men and women include genetics, medical conditions, medications, stress, and even childbirth. Even if you’ve never experienced hair loss, a change in your genes may cause thinning to begin in your 30s or 40s.
While your hair may have always been full and thick throughout your life, once you hit a certain age it just might stop growing entirely. Genetics can play a big role in the development of hair loss.
While some people may be more predisposed to the condition, the right combination of genetics and environmental factors may cause most people to experience hair thinning or loss at some point in their lives.
At a young age, hormones may be the main cause of diffuse thinning. For example, starting or stopping birth control or menopause can cause your hormones to shift. This may play a role in the development of hair loss due to the sudden change in hormone levels.
Types of Diffuse Thinning
There are different types of diffuse thinning hair loss. Here are some of the most common types:
Telogen effluvium:
Telogen effluvium is caused by an unexpected change in hormones and can happen when you’re pregnant, go on birth control, or experience menopause. It usually reverses itself once the hormones stabilize but it can cause significant hair loss or chronic telogen effluvium in the meantime.
Alopecia areata:
Alopecia Areata (diffuse alopecia Areata) is an autoimmune disease that causes sudden hair loss in patches. What causes it is unknown, but it can be treated with the help of a dermatologist.
Androgenic alopecia:
This is the most common type of hair loss in men and women. It usually starts with a receding hairline and progresses to complete baldness.
How to Prevent Diffuse Thinning?
If you want to try to prevent diffuse thinning from happening in the first place, there are several things you can do.
Eating a nutritious diet is one of the best ways to prevent hair loss, as it provides your body with the vitamins and minerals that keep your hair healthy.
Getting enough sleep is another good way to prevent hair loss since it helps your body repair itself.
Stress can also contribute to diffuse thinning, so it’s best to find ways to manage your stress.
Finally, protecting your hair from sun damage is important in preventing diffuse thinning, so wearing a hat when outside and applying sunscreen to your scalp when in the sun are two ways to do this.
Diffuse Hair Loss Treatment
There are many different hair loss treatments for diffuse thinning or diffuse hair loss. Depending on the cause, hair loss can be treated with a combination of diet, laser therapy, and hair transplants.
Diet plays an important role in hair loss treatment by keeping your scalp healthy. Poor nutrition can lead to inflammation and damage that can worsen hair loss. Certain vitamins and minerals can help fight hair loss, like vitamin B, iron, and zinc.
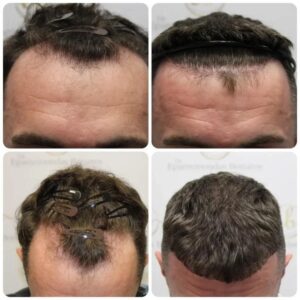
Hair transplants are another option for hair loss treatment. These work by replacing missing hair follicles with new ones. The procedure is most effective in conjunction with other treatments, such as laser therapy and hair restoration surgery.
Other options include topical treatments such as minoxidil or finasteride, or oral medications such as dutasteride or tetracycline. However, these treatments aren’t as effective as hair transplants which is a long term solution.
Minoxidil is less effective than laser therapy and may not work for everyone, so it’s important to talk to a professional about your options before you start using any medication or treatment for hair loss.
Conclusion
While multiple hair loss treatments may help, it is highly recommended that you talk to your doctor or a specialist to determine the option that is best for you. And if you’re dealing with this distressing type of hair loss it’s also important to find ways to cope with the stress that can come with it. You can book an online consultation too.