Alopecia areata is a common problem affecting about six million people in the United States alone. It can be emotionally unsettling and socially awkward when you have this condition. Especially the types affecting the scalp and face. For this reason, people affected usually seek prompt and lasting treatment.
In this article, we’ll be explaining what alopecia areata is, the types, symptoms, and signs, and the various treatments available.
Key Takeaways
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where your body fights the hair follicles on your skin leading to hair loss. The most common type is the patchy alopecia areata which presents with patchy areas of hair loss. Furthermore, the other less common types include totals, universalism, diffuse, and ophiasis alopecia areata.
Alopecia treatment focuses on hair regrowth using medications like corticosteroids, topical immunotherapy, and minoxidil. Alopecia treatment at home can also be instituted.
What Is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia means hair loss. ‘Areata’ is a Latin word that means a vacant space or a patch. Therefore, Alopecia areata is recurrent patchy hair loss from hair-bearing body regions. It usually manifests in different ways.
It is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the body produces an immune response against the hair follicles. Furthermore, air follicles are the structures in the skin that are responsible for producing hair. Also, there is evidence that the disorder is mostly hereditary.
Types of Alopecia Areata
It usually manifests in different forms, but in the main type, hair loss is typically in small patches. However, the other less common types include:
– Alopecia areata totalis:
Where the individual loses all the hair on the head(scalp). It looks like the male pattern of total baldness.
– Alopecia areata Universalis:
In this type, hair loss affects your whole body.
– Diffuse alopecia areata:
In this type, instead of losing the hair completely, the hair just thins out.
– Ophiasis alopecia areata:
Hair loss is in a distinctive band shape around the back and sides of your scalp.
Studies have shown that alopecia areata does not have a racial preference as it affects all races equally. Most times, onset is before 30 years. However, a study showed that the disease was more common in females.
Signs and Symptoms of Alopecia Areata

In most cases, alopecia areata is asymptomatic, meaning that those affected don’t show symptoms. However, some common symptoms you may experience include:
- Burning sensation or pruritus in the affected areas, usually before the hair falls out.
- Hairless patches can be single, double, or multiple.
- Fingernails and toenails may become brittle, reddish, and pitted.
Alopecia Treatments
Sadly, there is no cure for alopecia areata. But, Alopecia treatments are just for hair loss, and management is temporary. Thus, it stimulates the lost hair to regrow. However, treatment options for alopecia areata include:
– Corticosteroids
These are anti-inflammatory drugs for managing inflammatory diseases like autoimmune conditions. It works by reducing the rate at which your body destroys the hair follicles.
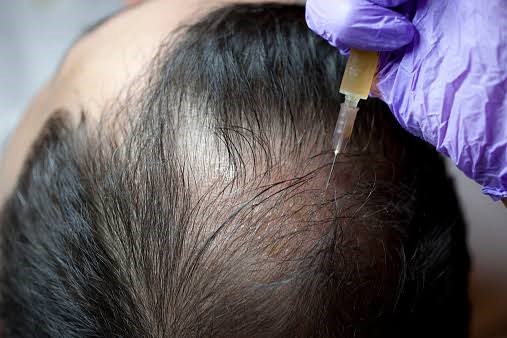
Application of corticosteroids into the affected area is said to be the most effective form of treatment. In addition, You can administer corticosteroids as a subcutaneous injection into the affected skin.
Injections are usually given just below the skin. The most widely used injectable corticosteroid for treating alopecia areata is Triamcinolone acetonide. It is injected into the site and repeated every four to six weeks.
– Topical Immunotherapy
In this treatment method, agents are applied to the affected skin to induce an allergic reaction. It is mostly used for severe cases or when there is a relapse after previous treatment. Studies have shown a success rate of about 30 to 50 percent, with regrowth occurring in about 12.2 months.
– Rogaine(Minoxidil)
Minoxidil finds use in people with extensive disease. The response rate is said to be between 8 to 45 percent. Regrowth usually begins in 12 weeks. However, continuous administration is necessary to maintain regrowth.
Other treatments include:
- Use of Anthralin
- Use of Prostaglandin analogs
- Systemic Treatments like Prednisone, Cyclosporine, and others.
- Use of light therapy
Alopecia Treatment at Home
Besides taking drugs, alopecia treatment at home include the following methods:
- Wearing hats, wigs, or scarves to cover the affected areas and protect you from excessive sun.
- Reduction of stress and anxiety. These have been said to trigger hair loss.
- Aromatherapy
- Use of probiotics
- Use of onion juice which is applied on the scalp
- You can use vitamins like biotin and zinc
- Use of topical gels and aloe vera drinks
- Use of herbal supplements such as green tea, ginseng, saw palmetto, and Chinese hibiscus.
Alopecia Treatment for Men
Alopecia areata is usually more extensive in men. Furthermore, a positive family history of A. A. is more common in men than women.
Alopecia treatment for men is usually focused on the affected body areas. Lastly, thesSites usually affected in men include:
- Scalp
- Face(beards)
- Chest
- Back
Alopecia Treatment for Women
As mentioned earlier, some studies show that alopecia areata is more common in females than males, and the reason is a mystery. Similarly, alopecia treatment for women is the same as in males, emphasizing the affected skin sites. Sites commonly affected include the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes people to lose hair. It is more common in females than in males. Additionally, it is more common in people less than 30 years.
Alopecia treatments focus on hair regrowth in both men and women as there is no cure for this condition. Injection or topical corticosteroids are most
If you have enjoyed this read, or you have any questions, please drop your comments in the comments section below.